Numerical Methods
The numerical methods are useful alternative procedures for solving math problems. Here are some important concepts for the development of numerical methods and all that implies, were taken as reference some websites and books, specializing in this field.
martes, 27 de julio de 2010
Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Capitulo 4
View more presentations from universidad industrial de santander.
View more presentations from Erika Villarreal
lunes, 10 de mayo de 2010
Chapter 3: Roots of Equations
Chapter 2: Numerical Approximation
Chapter 2
View more presentations from universidad industrial de santander.
Examples:
Example: pi is an irrational number, consisting of an infinite number of digits; 3.141592653589793 ... is a very good approximation of pi, which may be considered which is its exact value.
In considering the following approximations of pi:
- p = 3.15 is vague and inexact.
- p = 3.14 is exact but imprecise.
- p = 3.151692 is precise but inexact.
- p = 3.141593 is exact and precise.
The numerical methods should provide sufficiently exact and precise solutions. The error term is used to represent the inexactitude and to measure the uncertainty in the prediction.
Chapter 1: what is a modeling?
It is a process to create a model to make or understand something. A mathematical modeling is then defined as a process from the mathematical point, of view in which describes a real-world fact; the main objective is to understand that process and also to predict its behavior in the future.
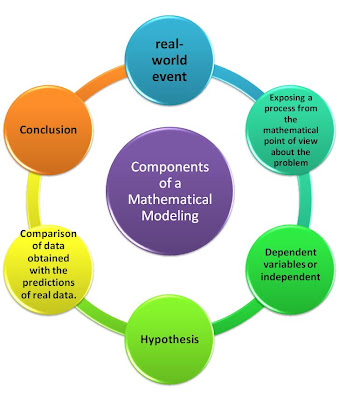
The differential equations as mathematical modeling.
When the hypothesis is raised, implies the reason or rate of change of one or more variables involved. Therefore, the mathematical statement of this hypothesis is one or more equations, which involved, derivative, ie, differential equations.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)
